- Start with a blank document
- Existing Document (i.e, from an existing biosketch)
- External source (eRA Commons, ORCiD, NSF)
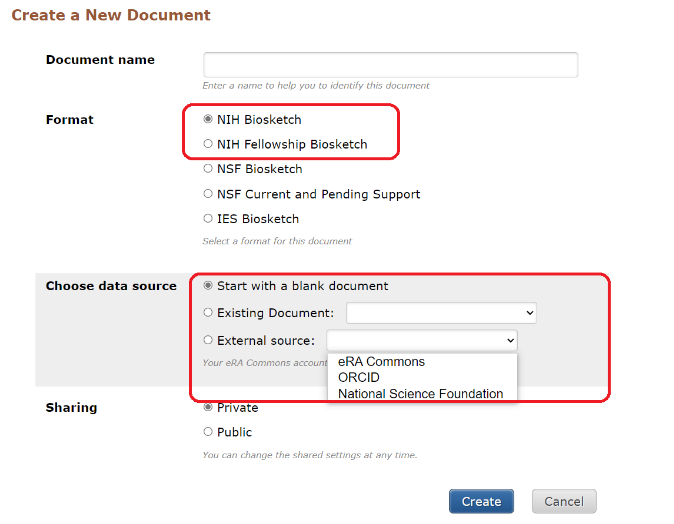
SciENcv is connected to My Bibliography, and can be connected with ORCiD too. Users can directly import up to four desired citations from either My Bibliography or ORCiD into their biosketches.
Notes: Biosketch Creation
- SciENcv is not required for creating a NIH biosketch in the new format.
- Users are recommended to have their My Bibliography accounts created and updated before using SciENcv to create a biosketch.
- SciENcv users can also create biosketches using data stored in their ORCID records. By linking an ORCID account to an NCBI account, users will be able to auto-populate biosketches using the personal statement, education, employment, publications and research awards information stored in ORCID records. See My NCBI – ORCID Author Data Integration with SciENcv.
Links for Creating Biosketches Using SciENcv
More information about SciENcv
Option 2 - Using a Word Template to Create NIH Biosketches
Researchers can opt to use a blank template in Word to create a Biographical Sketch Format Page. Links to the blank format page are provided below (along with instructions, samples, FAQs and other resources).
For Non-Fellowship Biosketch:
- Non-fellowship Biosketch (blank format page, Word)
- Instructions for Biographical Sketch
These instructions will be incorporated into the NIH Application Form Instructions with the next update by FY 2022. - SAMPLE: Non-fellowship biosketch
- FAQs
- NIH Pre-award and Post-award Disclosures Relating to the Biographical Sketch and Other Support
For Fellowship Biosketch:
- Fellowship Biosketch (blank format page, Word)
- Instructions for Biographical Sketch
These instructions will be incorporated into the NIH Application Form Instructions with the next update by FY 2022. - Predoctoral Fellowship biosketch sample (Word)
- Postdoctoral Fellowship biosketch sample (Word)
- FAQs
- NIH Pre-award and Post-award Disclosures Relating to the Biographical Sketch and Other Support
- the name and location of the institution
- the degree received (if applicable)
- the month and year of end date (or expected end date). For fellowship applicants only, also include the month and year of start date.
- the field of study (for residency entries, the field of study should reflect the area of residency training)
Following the education block, complete Sections A-D of the biographical sketch
Section A: Personal Statement
- If you wish to explain factors that affected your past productivity, such as family care responsibilities, illness, disability, or military service, you may address them in this "A. Personal Statement" section.
- Indicate whether you have published or created research products under another name.
- You may mention specific contributions to science that are not included in Section C. (Do not present or expand on materials that should be described in other sections of this Biosketch or application.)
- Figures, tables, or graphics are not allowed.
Note the following instructions for specific subsets of applicants/candidates:
- For institutional research training, institutional career development, or research education grant applications: Faculty who are not senior/key persons are encouraged, but are not required, to complete the "A. Personal Statement" section.
- For dissertation research awards (e.g., R36), Applicants should, in addition to addressing the points noted above, also include a description of their career goals, their intended career trajectory, and their interest in the specific areas of research designated in the FOA.
- Candidates for research supplements to promote diversity in health-related research should, in addition to addressing the points noted above, also include a description of their general scientific achievements and/or interests, specific research objectives, and career goals. Indicate any current source(s) of educational funding.
- Students, postdoctorates, and junior faculty should include scholarships, traineeships, fellowships, and development awards, as applicable.
- Clinicians should include information on any clinical licensures and specialty board certifications that they have achieved.
Section C: Contributions to Science
- the historical background that frames the scientific problem;
- the central finding(s);
- the influence of the finding(s) on the progress of science or the application of those finding(s) to health or technology; and
- your specific role in the described work.
- Figures, tables, or graphics are not allowed.
For each contribution, you may cite up to four publications or research products that are relevant to the contribution. If you are not the author of the product, indicate what your role or contribution was. Note that while you may mention manuscripts that have not yet been accepted for publication as part of your contribution, you may cite only published papers to support each contribution. Research products can include audio or video products (see the NIH Grants Policy Statement, Section 2.3.7.7: Post-Submission Grant Application Materials); conference proceedings such as meeting abstracts, posters, or other presentations; patents; data and research materials; databases; educational aids or curricula; instruments or equipment; models; protocols; and software or netware. Use of hyperlinks and URLs to cite these items is not allowed.
It is permissible to cite interim research products. Note: Interim research products have specific citation requirements. (See related Frequently Asked Questions for more information.)
You may provide a URL to a full list of your published work. This URL must be to a Federal Government website (.gov). Providing a URL to a list of published work is not required; however, if desired, then NIH recommends using My Bibliography. See the "URL to Published Works" tab for more information on providing a link to a list of published works.
Descriptions of contributions may include a mention of research products under development, such as manuscripts that have not yet been accepted for publication. These contributions do not have to be related to the project proposed in this application.
*Section D: Scholastic Performance
- applicants for predoctoral and postdoctoral fellowships
- applicants to dissertation research grants (e.g., R36)
- candidates for research supplements to promote diversity in health-related research from the undergraduate through postdoctoral levels
Scholastic Performance
Predoctoral applicants/candidates (including undergraduates and post-baccalaureates): List by institution and year all undergraduate and graduate courses, with grades. In addition, explain any grading system used if it differs from a 1-100 scale; an A, B, C, D, F system; or a 0-4.0 scale. Also indicate the levels required for a passing grade.
Postdoctoral applicants: List by institution and year all graduate scientific and/or professional courses with grades. In addition, explain any grading system used if it differs from a 1-100 scale; an A, B, C, D, F system; or a 0-4.0 scale. Also indicate the levels required for a passing grade.
URL to Published Works

The Contributions to Science Section offers investigators the option to include a URL to a full list of published work. NIH recommends that investigators use "My Bibliography" as NIH can assure reviewers that their anonymity will be protected if they review publications at that site. A URL for a publication list is optional and, if provided, must be to a government website (.gov) such as My Bibliography. Template:
- Use the My Bibliography “Sharing” feature to obtain a URL.
- Click the “Make it Public” link.
- A URL will appear.
- Copy and paste the entire URL string to the template.
- Private/Public settings are flexible.

- Check the box below the Contributions to Science section.
Include link to complete list of published work in My Bibliography.
(Selecting this option will make the list public.)
- Spell the URL in full, beginning with "http://."
- Do not embed the link as hyperlinked text. The link will not remain active after processing.
- The URL to a full list of published work is not required.
- Only one URL is allowed in the Biosketch. Any URLs other than the List of Published Works to a government website will not be allowed.
My Bibliography
- save references of their scholarly works directly from PubMed
- add references manually using the built-in template
If your NCBI account is linked to eRA Commons, you can use your My Bibliography to view whether your publications comply with the NIH Public Access Policy, start the compliance process for applicable journal articles if not in compliance, and associate your publications to awards when applicable.
You may add a delegate in your NCBI account to manage your My Bibliography.
ORCID
ORCID (pronounced "orkid") stands for Open Researcher and Contributor ID. ORCID is an open, non-profit, and community-driven effort to create and maintain a registry of unique researcher identifiers. An ORCID iD acts as a unique identifier for a person, much like each publication in PubMed has a PubMed ID. Why do I need an ORCID identifier (ORCID iD)? While not mandatory, publishers and funding agencies are increasingly adopting ORCID as a tool to manage submissions and applications. At some point in the future, having an ORCID iD and using ORCID as a tool may be required. Note: ORCID is currently required for NIH fellowship and Career Development applications. An ORCID iD is unique, and it distinguishes you from other researchers with similar or the same names. On average, a name in PubMed could be referencing 8 authors. Having an ORCID, you can quickly identify which publications are yours. ORCID is also transferrable to other institutions. For new researchers, an ORCID iD offers a way to have an accurate record of your scholarly output from the very beginning. You can use it on your CV, departmental webpage, email signature, in professional directories and more. How do I create an ORCID iD? Once your ORCID ID has been created, click on the Create or Connect your ORCID ID link in your Commons Personal Profile and log into ORCID. You will then be prompted to authorize NIH to access your personal ORCID profile (as illustrated below).

- Search and link
- Add DOI
- Add PubMed ID (PMID)
- Add BibText
- Add manually
Adding a Delegate
Researchers are able to add one or more delegates or proxy in ORCID to manage their ORCID records and updating scholarly works. To add a delegate, go to Account Settings, scroll down to Trusted Individuals. Add the name or email address in the box below Trusted Individuals. Other ORCID users can grant permission for you to update their records. A trusted individual does not need to be another researcher but must have an ORCID iD.
Overview
- Resources and/or financial support from all foreign and domestic entities, that are available to the researcher. This includes but is not limited to, financial support for laboratory personnel, and provision of high-value materials that are not freely available (e.g., biologics, chemical, model systems, technology, etc.). Institutional resources, such as core facilities or shared equipment that are made broadly available, should not be included in Other Support, but rather listed under Facilities and Other Resources.
- Consulting agreements, when the PD/PI or other senior/key personnel will be conducting research as part of the consulting activities. Non-research consulting activities are not Other Support.
- In-kind contributions, e.g. office/laboratory space, equipment, supplies, or employees or students supported by an outside source. If the time commitment or dollar value of the in-kind contribution is not readily ascertainable, the recipient must provide reasonable estimates.
Other support does not include training awards, prizes, or gifts. Gifts are resources provided where there is no expectation of anything (e.g. time, services, specific research activities, money, etc.) in return. An item or service given with the expectation of an associated time commitment is not a gift and is instead an in-kind contribution and must be reported as such.
Other Support information is requested for:
- All individuals designated in an application as senior/key personnel, except
- Program Directors, training faculty, and other individuals involved in the oversight of training grants
- Individuals categorized as Other Significant Contributors
- All senior/key personnel, excluding consultants, in progress reports when there has been a change in active other support, except
- Program Directors, training faculty, and other individuals involved in the oversight of training grants
Updated Requirements Effective January 25, 2022 (NOT-OD-21-073)Effective January 25, 2022, NIH requires the following:
- Supporting documentation, which includes copies of contracts/agreements specific to senior/key-personnel foreign appointments and/or employment with a foreign institution for all foreign activities and resources that are reported in Other Support. If the contracts/agreements are not in English, recipients must provide translated copies.
- Immediate notification of undisclosed Other Support. When a recipient organization discovers that a PI or other Senior/Key personnel on an active NIH grant failed to disclose Other Support information outside of Just-in-Time or the RPPR, as applicable, the recipient must submit updated Other Support to the Grants Management Specialist named in the Notice of Award as soon as it becomes known.
Additional information on Other Support can be found in the Grants Policy Statement.
Using the NIH Word Template to Create Other Support
- Instructions for Biographical Sketch
- Instructions for Biographical Sketch

