We are pleased to share with you the 25 most downloaded Nature Communications articles* in the life and biological sciences published in 2023. (Please note we have a separate collection for the Top 25 COVID-19 papers.) Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an international community.
*Data obtained from SN Insights (based on Digital Science's Dimensions) and have been normalised to account for articles published later in the year.

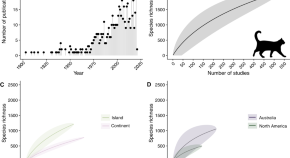
Free-ranging domestic cats have major ecological impacts globally. Here, Lepczyk et al. compile records of the species consumed by cats, identifying thousands of species consumed, including hundreds of species that are of conservation concern.
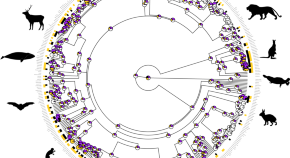
There is still no consensus on the factors favouring the evolution of same-sex sexual behaviour in mammals. This study presents evidence that it is a widespread behaviour that has evolved repeatedly in mammals, and that may play an adaptive role in bonding and conflict resolution.

Nail polish dryers commonly emit ultraviolet A (UVA) light, but the effects of this irradiation on mammalian cells remain unclear. Here, the authors examine the effects of UVA irradiation by a nail polish dryer on the genomes of mammalian cell lines, finding high levels of reactive oxygen species and related mutational signatures.
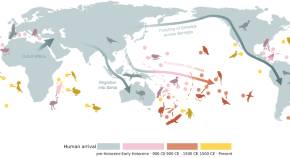
The true number of human-driven bird extinctions is likely larger than we think. Here, the authors combine recorded extinctions with estimates from the fossil record to suggest that ~1400 bird species have gone extinct since the Late Pleistocene.

The integration of single-cell and spatial data can provide a more comprehensive picture of the network of cells within the tumour microenvironment. Here the authors use a combination of single-cell and spatial technologies including 10x Xenium to characterise serial formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human breast cancer sections.
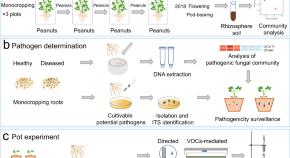
Crop rotation helps preventing pathogen infestations compared to monocultures, which may be partly due to root-associated microbes. Here, the authors show that rhizosphere microbiomes in monocultures are less able to suppress fungal pathogens compared to crop rotations, and that inoculating certain microbes can mitigate it.
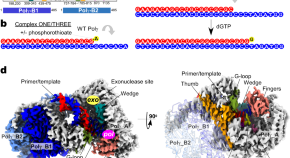
Here, the authors use cryo-EM to capture nine intermediates along the DNA proofreading pathway using human mitochondrial DNA Polymerase Gamma. The results provide a step-by-step view of the DNA proofreading at single-nucleotide resolution.
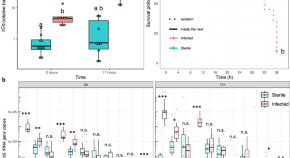
Infected wounds pose a major mortality risk in animals and are common in predatory ants. Here, the authors show that M. analis ants apply antimicrobial compounds produced in the metapleural glands to treat infected wounds and reduce nestmate mortality.
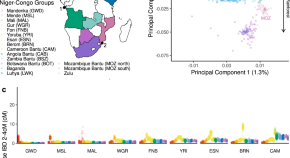
African human genome variation remains under-sampled. Here, the authors present a collection of 350 whole genome sequences from Angola and Mozambique and model the timing and extent of significant demographic events in African history.

Here the authors present the structural mechanism of recognition of unnatural nucleobases in a six-letter expanded genetic system by E. coli RNA polymerase, and provide structural evidence for tautomerization during transcription.
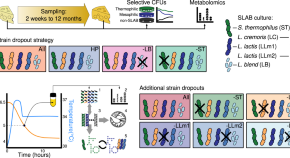
Cheese fermentation and flavour formation are the result of complex biochemical reactions driven by the activity of multiple microorganisms. Here, the authors identify microbial interactions as a mechanism underlying flavour formation in Cheddar cheese.
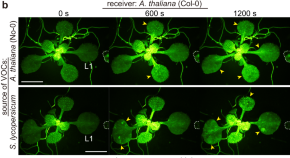
Plants sense volatiles emitted by injured neighboring plants and elicit defense responses to external threats. Here, the authors show that Arabidopsis leaves uptake two green leaf volatiles via stomata and trigger cytosolic Ca 2+ defense signaling.
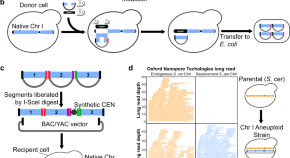
Building synthetic chromosomes from natural components is an unexplored alternative to de novo chromosome synthesis that may have many potential applications. In this paper, the authors report CReATiNG, a method for constructing synthetic chromosomes from natural components in yeast.
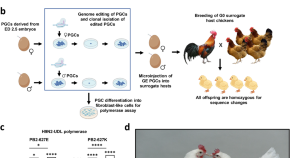
In chickens, influenza A virus relies on host protein ANP32A. Here the authors use CRISPR/Cas9 to generate homozygous gene edited chickens containing two ANP32A amino acid substitutions that prevent viral polymerase interaction.
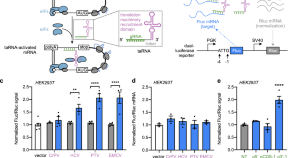
Many diseases are driven by the insufficient expression of critical genes, but few technologies are capable of rescuing these endogenous protein levels. Here, Cao et al. present an RNA-based technology that boosts protein production from endogenous mRNAs by upregulating their translation.
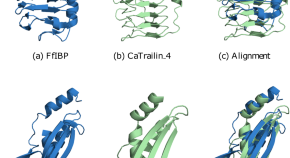
Will protein structure search tools like AlphaFold replace protein sequence search with BLAST? We discuss the promises, using structure search for remote homology detection, and why protein BLAST, as the leading sequence search tool, should strive to incorporate structural information
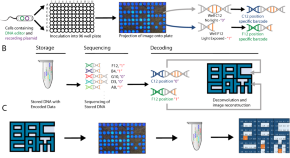
DNA data storage has gained recent interest due to the high information density of DNA. Here, the authors have developed a method to directly capture information in the form of light and encode it into DNA via bacteria, analogous to a digital camera.
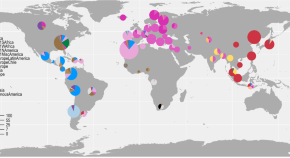
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori, often found in the human stomach, can be classified into distinct subpopulations associated with the geographic origin of the host. Here, the authors provide insights into H. pylori population structure by collecting over 1,000 clinical strains from 50 countries and generating and analyzing high-quality bacterial genome sequences.

The integration of spatial, imaging, and sequencing information enables the mapping of cellular dynamics within a tissue. Here, authors show three algorithms in stLearn software to accurately reveal spatial trajectory, detect cell-cell interactions, and impute missing data.
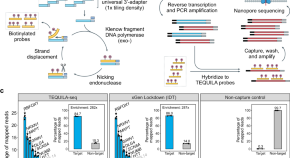
The authors report TEQUILA-seq, a versatile, easy-to-implement, and low-cost method for targeted long-read RNA sequencing. TEQUILA-seq uncovers transcript isoforms and RNA mechanisms associated with human health and disease.
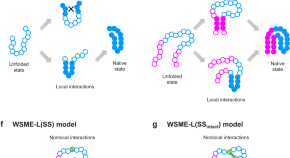
Predicting how proteins fold into specific native structures remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a simple physical model that accurately predicts protein folding mechanisms, paving the way for solving the folding process component of the protein folding problem.
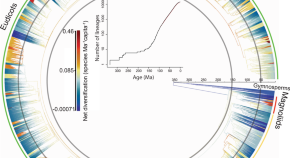
Global spatiotemporal patterns of plant diversification are unclear. Here, the authors use a genus-level phylogeny and global distribution data for 14,244 flowering plant genera, finding a negative correlation between spatial patterns of diversification and genus diversity.
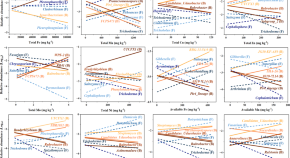
Soil micronutrients may be important for belowground biota and associated functions. Here, the authors identify the relationships between metallic micronutrients and soil microbial communities and functions across 180 sites, and validate them in a soil incubation experiment.
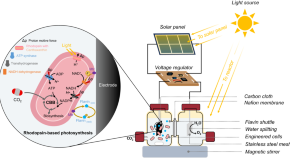
Microbial rhodopsins are major contributors to global light harvesting on Earth, but their role in carbon fixation is unclear. Here, the authors construct an artificial photosynthesis system by combining rhodopsin with an extracellular electron uptake mechanism for photoelectrosynthetic CO2 fixation in Ralstonia eutropha.
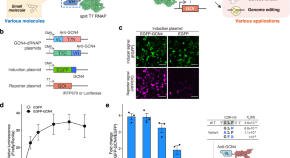
Controlling gene expression in response to the intracellular molecule of interest is challenging. Here, the authors repurposed antibody variable regions to control gene expression in an inducible manner by combining them with a split RNA polymerase.